Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an advanced form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease that commonly goes undetected and leads to serious consequences such as liver transplant. Explore your NASH clinical research participation options.

In the early stages of fatty liver disease, there are typically minimal or no symptoms. This allows fatty liver to progress to NASH.
Individuals at greatest risk of developing NASH are those who are obese, have high blood sugar, and high cholesterol.

NASH is the 2nd leading cause of liver transplants in the U.S.
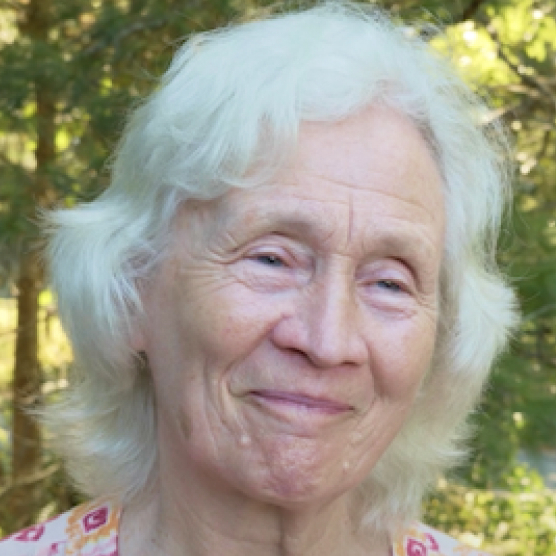

"I wholeheartedly hope other people will step up and do it, so they have enough people to fully carry this through."
Penny
Clinical Trial Participant
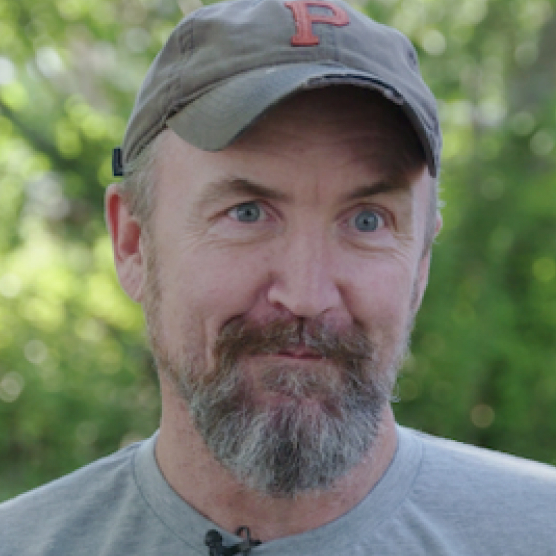

"I think that people should try to help other islanders by getting this study going, and I think you should do it."
Mike
Clinical Trial Participant

“People have to step up and be part of the solution.
It’s nothing to be afraid of.”
Kathleen
Clinical Trial Participant
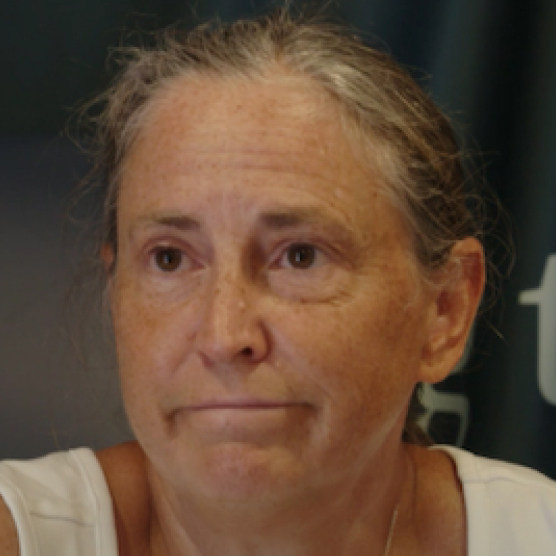

"We need people to participate in studies to be able to get these things out there and get them approved."
Janet
Clinical Trial Participant
Testimonials provided by trial participants are personal experiences and do not necessarily represent the views of the trial sponsor or Care Access. They are not a substitute for medical advice, and the results of the trial may vary based on individual circumstances. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any medical decisions.

Why wait to help impact the future of NASH care? Participants may receive:

Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is an advanced form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that commonly goes undetected until the liver is severely damaged and leads to serious consequences such as liver transplant.
The symptoms of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) include intense itching, abdominal swelling, easy bruising and bleeding, jaundice, and varicose veins. Behavior changes, confusion, and slurred speech are also symptoms of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
There are no treatments for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) currently, but weight loss can reduce fat and inflammation of the liver. Researchers are working on treatments so consider joining a research study to help advance medicine for NASH.
People who are at risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are people older than 50, are obese, and who have certain genetic risk factors.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is the term for a range of conditions caused by a build-up of fat in the liver. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is usually seen in people who are overweight or obese as a healthy liver should have little to no fat.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease symptoms include itchy skin, abdominal swelling, shortness of breath, swelling of the legs, varicose veins, enlarged spleen, red palms, and jaundice.
Currently, there are no approved nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatments, so physicians work to treat the underlying conditions such as obesity. There are also some self-care options like low carbohydrate/low fat diet and dietary supplements. Join a research study to explore potential nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatments.